Chang'e-3
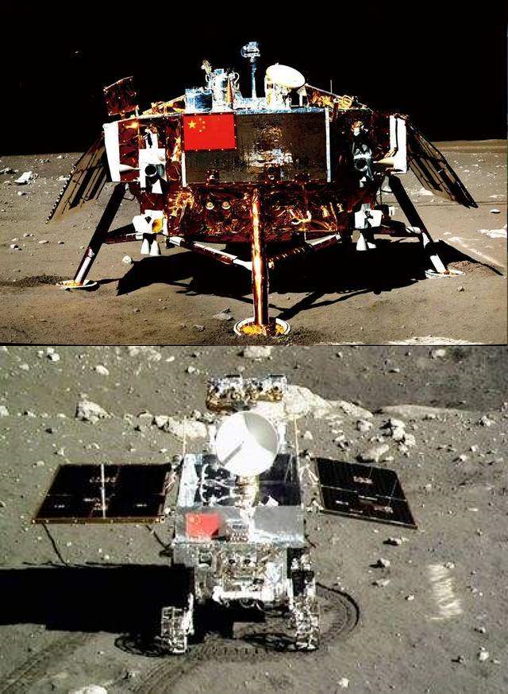
The Chang'E-3 is an unmanned lunar exploration mission incorporating a robotic lander and China's first lunar rover. It was launched on December 2, 2013 as part of the second phase of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program. On 14 December 2013, The Chang'E-3 landed on the lunar surface near Sinus Iridum, becoming the first spacecraft to soft-land on the Moon since the Soviet Union's Luna 24 in 1976. The scientific objectives of the Chang'E-3 include lunar surface topography and geology survey, lunar surface material composition and resource survey, Sun-Earth-Moon space environment detection, and lunar-based astronomical observation.
There are 4 scientific payloads on the lander: Moon-based Ultraviolet Telescope (MUVT), Extreme Ultraviolet Camera (EUVC), Terrain Camera (TCAM), Landing Camera (LCAM), and 4 scientific payloads on the rover: Panoramic camera (PCAM), Active Particle-induced X-ray Spectrometer (APXS), Lunar Penetrating Radar (LPR), Visible and Near-infrared Imaging Spectrometer (VNIS). Full details are given as followed.
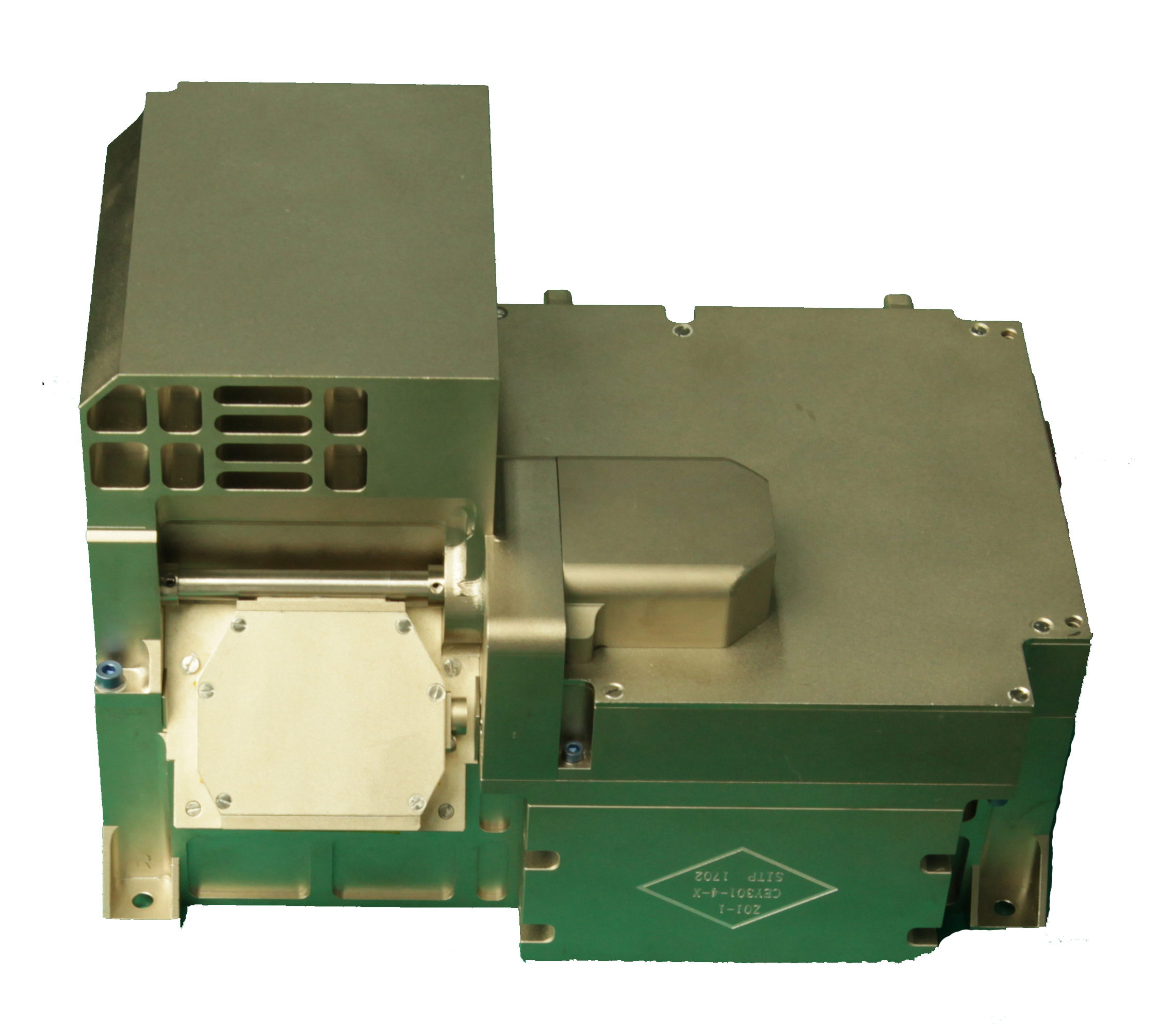
MUVT
| Moon-based Ultraviolet Telescope (MUVT) onboard the lander is used to observe galaxies, binary stars, active galactic nuclei and bright stars. The MUVT system is the first long-term observatory to be deployed on the Moon. MUVT is the only payload of CE-3 still working till now. |

EUVC
| Extreme Ultraviolet Camera (EUVC) onboard the lander can image the plasmasphere of the Earth from varied angles in the EUV wavelengths and obtain side view EUV images of the plasmasphere, such observation is made for the first time on the lunar surface. |

TCAM
| Terrain Camera (TCAM) is one of the lander's major scientific payloads installed on the pointing mechanism of the lander, to conduct color imaging and dynamic photography for its scientific goal of investigating the morphology and geologic structure of the lunar surface together with the other two camera payloads. |

LCAM
| Landing Camera (LCAM) is mounted at the bottom of the lander, the scientific goal of LCAM is to obtain image data during the lander descent from an elevation range of 12 km to 3m, which is used for precise positioning of the landing site and target selection of the rover survey. |

PCAM
| Panoramic camera (PCAM) is one of the rover's major scientific payloads, with two cameras installed on the mast of the Yutu rover, and has the ability to take color and panchromatic images to investigate the morphology of the lunar surface around the landing site. |

APXS
| The Active Particle-induced X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) is an important payload mounted on the Yutu rover, which is part of the Chang'E-3 mission. The scientific objective of APXS is to perform in-situ analysis of the chemical composition of lunar soil and rock samples. |

LPR
| Lunar Penetrating Radar (LPR) is one of the payloads onboard the Chang'E-3 (CE-3) rover, which is the first attempt to explore the lunar subsurface structure by using ground penetrating radar with high resolution. A depth of several hundred meters to the subsurface have been probed using the LPR. |
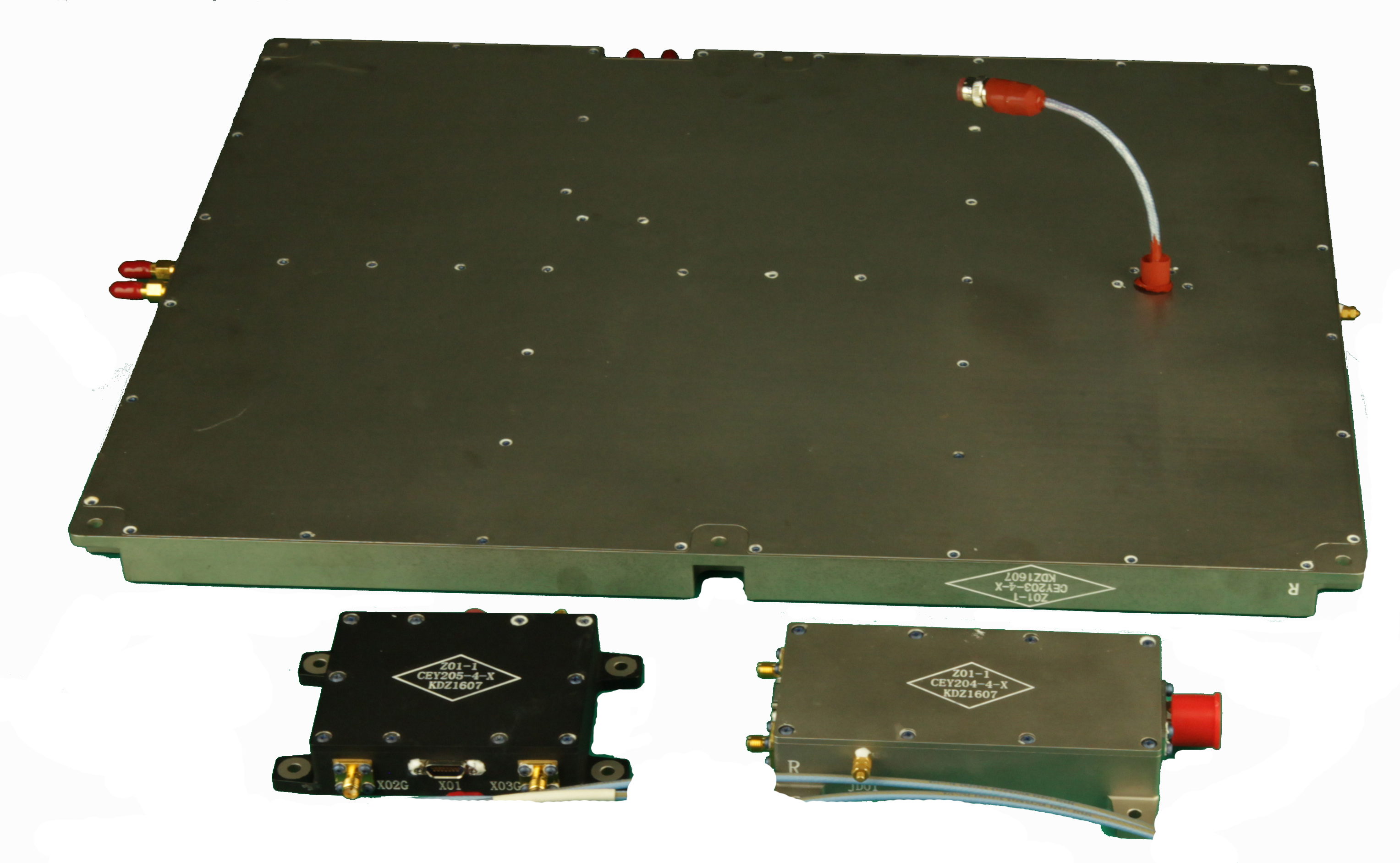
VNIS
| Visible and Near-infrared Imaging Spectrometer (VNIS) is one of the four payloads on the Yutu rover. After traversing the landing site during the first two lunar days, four different areas are detected. VNIS is the first instrument used for in-situ analysis in a lunar exploration mission which carried an AOTF for spectroscopic analysis. |
Data Introduction:https://vsso.nssdc.ac.cn/nssdc_en/html/vssolist.html?searchKeywords=Chang%27E-3
Data Access:https://moon.bao.ac.cn/web/enmanager/home