Gravitational wave high-energy Electromagnetic Counterpart All-sky Monitor (GECAM)
The satellite project of gravitational wave high-energy electromagnetic counterpart all sky monitor (GECAM) is one of the scientific satellites approved by the strategic leading science and technology project "Space Science (phase II)" of Chinese Academy of Sciences. On December 4, 2018, the project was officially approved by the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The project is planned to be launched by the end of 2020, and the satellite will be in orbit for three years.
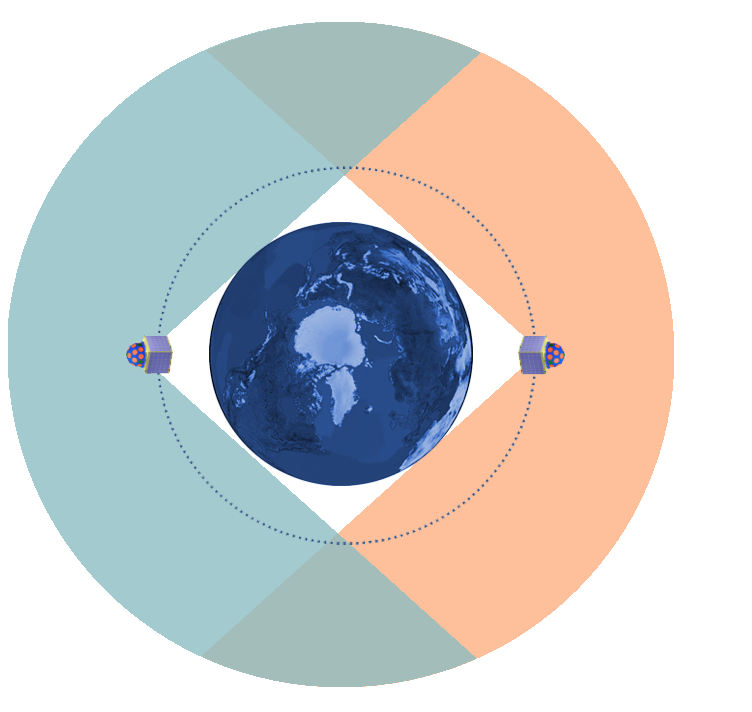
GECAM satellite specially aims at the research opportunity of gravitational wave gamma ray bursts (i.e., high-energy electromagnetic counterpart of gravitational waves). Through the layout of two satellites on both sides of the earth, it monitors the high-energy radiation phenomena such as gravitational wave gamma bursts in orbit, and solves the mystery of intense merging of dense celestial bodies in the universe. At the same time, we can understand the mechanism of solar bursts, solar bursts, solar bursts, and so on.The project was launched on December 10, 2020 and the satellite will be in orbit for three years.

1. The high-energy electromagnetic correspondents of gravitational wave events are monitored throughout the day, and the largest sample of gravitational wave gamma bursts and new radiation phenomena are found. The dense celestial bodies such as neutron stars and black holes and their merging processes are studied;
2. The possible high-energy radiation of the fast radio storm is monitored all day to reveal its physical origin and radiation mechanism;
3. All kinds of special GRBs and magstar bursts are monitored all the time, and their burst mechanisms are studied in depth.
4. Other scientific objectives
Monitoring hundreds of X-ray / gamma ray sources
Monitoring of solar flare (SFL) wide band radiation
The earth gamma ray flash (TGF) and earth electron beam (TEB) were monitored.
1. Satellite and its main technical indicators
GECAM satellite adopts two low orbit microsatellites in conjugate constellation layout on both sides of the earth. It has full-time all day field of view, high sensitivity (2e-8 ERG / cm2 / s), good positioning ability (~ 1 degree), wide band energy spectrum measurement ability (8 kev-2 MeV) and the ability to distinguish between gamma ray bursts and space charged particle events. It will find all kinds of gravitational wave gamma bursts with the largest sample.
Scientific exploration orbit: the orbit of the two satellites is the same, with the opposite phase, the orbit altitude is 600km, and the inclination angle is 29 °
Total mass of Double Star: no more than 360kg
Launch time: December 2020
Rocket: Solid Launch Vehicle
Satellite life: no less than 3 years
2. Scientific exploration payload
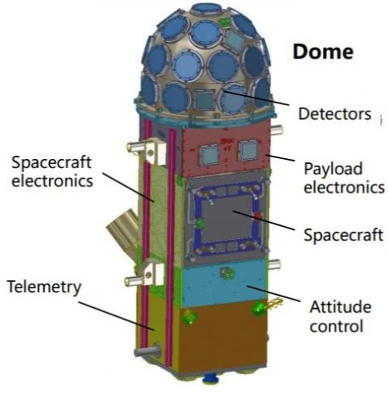
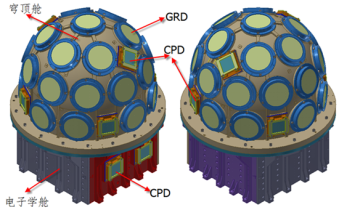
The payload system of GECAM satellite is composed of gamma ray detector (GRD), charged particle detector (CPD), load processor and main structure of payload.
Among them, gamma ray detector (GRD) and charged particle detector (CPD) are scientific detection payloads.
Gamma ray detector (GRD): it adopts modular design, with 25 detector modules pointing to different directions respectively to achieve large field of view, good positioning ability and wide energy area coverage. It can realize 8 keV ~ 2 MeV gamma ray detection, measure the light variation and energy spectrum of gamma ray bursts, and locate the gamma ray bursts. Charged particle detector (CPD): composed of eight charged particle detectors, it can identify space charged particle events and remove its interference to gravitational wave gamma storms.
Load processor: it is used to collect and process GRD and CPD signals, to trigger and locate GRD and CPD signals in orbit, and to transmit astronomical warning in quasi real time; to realize data storage, transmission and interaction with satellite platform.
Data Introduction:https://vsso.nssdc.ac.cn/nssdc_en/html/vssolist.html?searchKeywords=GECAM
Data Access:https://gecam.nssdc.ac.cn